graph LR
subgraph Submitter
A["**Not Started**"] --> B["**In Progress**"]
B --> C["**Ready for Review**"]
end
subgraph Reviewer
C --> D["**Reviewed**"]
D -.-> B
end
subgraph Approver
D --> E["**Signed Off**"]
end
Working with attestations
Attestation enables submitters, reviewers, and approvers to formally certify, review, and sign off on model attributes at specific points in time, supporting compliance and governance processes.
Prerequisites
-
- Customer Admin — Sets up attestations
- Submitter — Stakeholder who submits attestation questionnaires
- Reviewer — Organizational role that reviews attestation questionnaires
- Approver — Organizational role that approves attestation questionnaires
Key concepts
- attestation
- A formal process where attestation participants certify key model information at a specific time. Attestation is part of your audit trail and confirms that governance, documentation, and control requirements are met.
- attestation instance
- The invocation of the attestation process on the ValidMind Platform. Created when the attestation is triggered by the schedule you set up, it includes a snapshot with model activity and artifacts, questionnaire responses and review status, forming a full record of the review and approval process.
- attestation participant
- A user assigned to one of three roles in the attestation workflow — submitter, reviewer, or approver. Submitters must be model stakeholders; reviewers and approvers can be assigned by stakeholder or role.
- attestation period
- The time window during which attestation is active, with fixed start and end dates. Each period creates an unchanging model snapshot. Periods are usually scheduled quarterly or annually and can align with regulatory or internal cycles.
- attestation questionnaire
- A structured form that submitters use to confirm model status, documentation and compliance. It supports formatted inputs like checkboxes and text fields, serving as both a compliance check and formal review record.
- execution schedule
- The mechanism, manual or automated, that starts the attestation process based on set periods. It creates attestation instances, triggers snapshots and begins the workflow for attestation participants.
- group
- An organizational unit that associates models with specific teams or functions. When reviewers or approvers are assigned by role, they can only act on models within groups they belong to — resulting in one attestation submission per model owner per group.
- inventory scope
- The filter conditions that define which models are included in an attestation. Scope can be set using rules based on model fields, stages, or custom attributes.
- snapshot
- A fixed capture of model data at a specific time. It includes optional custom fields and related artifacts and stays unchanged throughout the attestation, ensuring historical accuracy.
Where do I access attestations?
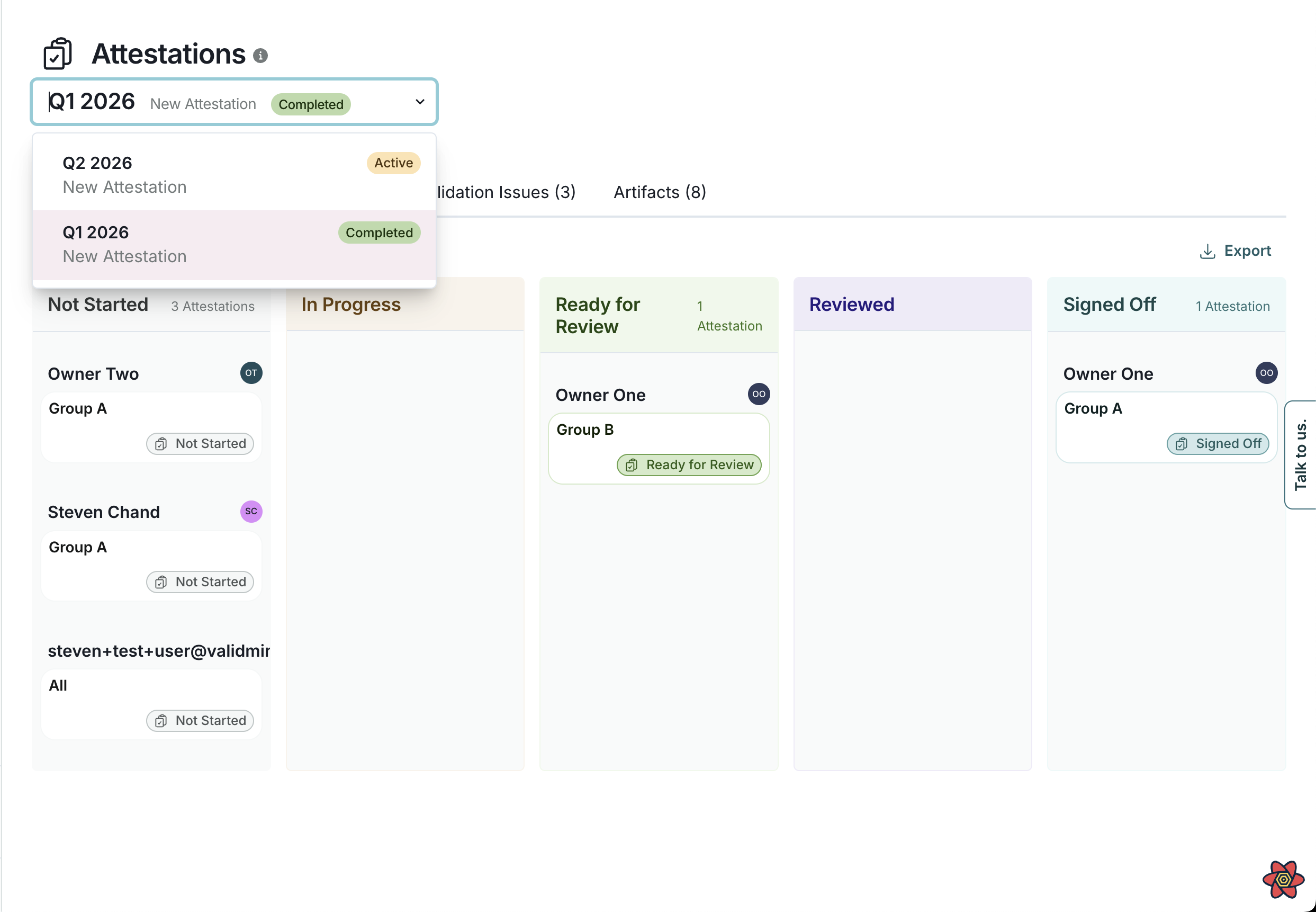
When an attestation period is active or has been completed in the past, Attestations appears in the left sidebar. This centralized dashboard provides:
- A swimlane view of all attestation submissions organized by status
- Consolidated questionnaire responses across all submissions
- Organization-wide snapshots of models, validation issues, and artifacts
- Export capabilities for compliance reporting
Attestation participants can also access their individual tasks via My Inbox in the left sidebar, where tasks appear under the Tasks tab with the current attestation status.
The Attestations sidebar item only appears when there is at least one active or completed attestation period. If your organization has not yet configured attestations, this option is not visible.
How does the attestation process work?
Attestation on the ValidMind Platform begins at the start of the attestation period after the process has been set up initially. The platform captures a snapshot of each model and its artifacts, preserving the state at that point in time. A second snapshot is captured when the attestation period is completed, enabling comparative analysis between the start and end states.
Responsibilities for the attestation process are shared:
The attestation process — Submitter, reviewer, and approver responsibilities
The submitter is responsible for completing the questionnaire and addressing change requests. The reviewer is responsible for reviewing the questionnaire and requesting any necessary changes. The approver is responsible for signing off on the questionnaire.
Plan your attestation periods ahead of time to ensure they can be completed on time. The start date must be today or a future date, and you cannot set a date in the past to trigger attestation retroactively.
How are attestation submissions organized?
Attestation submissions are organized by owner AND group. This structure supports organizations where:
- Model owners may own models across multiple groups, such as Fraud and Know-Your-Customer (KYC).
- Each group has its own validation and governance team.
- Reviewers and approvers are roles scoped to specific groups.
How do I create meaningful attestation questionnaires?
Attestation questionnaires are typically used in model risk management to confirm that key controls, governance processes and documentation requirements have been followed throughout a model’s lifecycle. These questionnaires are part of a broader effort to ensure accountability and regulatory compliance.
Questionnaires are composed of structured fields that you define when configuring the attestation template. Each field can be a text input, dropdown, checkbox, or other field type, with optional validation rules. Responses are collected consistently across all submissions and can be viewed in the consolidated Responses tab or exported for external reporting.
Areas typically covered in the questionnaire:
Verification of responsibilities — Attests that model owners, developers and validators have performed their roles in accordance with internal policies and procedures.
Documentation of compliance — Confirms that required documentation — such as model documentation, validation reports and change logs — has been completed and properly archived.
Evidence of control operation — Serves as formal evidence that key controls (for example: backtesting, performance monitoring, version control) are in place and functioning as intended.
Governance checkpoints — Used as checkpoints at critical stages, such as model approval, annual reviews or retirement, to ensure all required steps have been completed before proceeding.
Regulatory reporting — In regulated environments, provides a documented trail that can be reviewed during internal audits or by external regulators.
Risk ownership and accountability — By signing off on questionnaires, individuals acknowledge their responsibilities and support a strong control culture.
Work with your model risk management team to create a template that accurately reflects your organization’s attestation requirements.